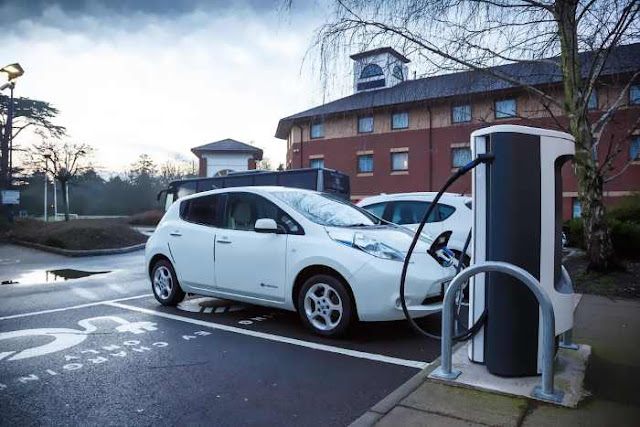
Electric Vehicle Charging: Problems and Solutions
As the world progresses towards a greener future, electric vehicles (EVs) have become increasingly popular. But with this rise in popularity comes the need for more EV charging stations. In this article, we will discuss everything you need to know about electric vehicle charging.
Electric vehicles (EVs) are quickly becoming a more common sight on our roads, but without the proper infrastructure, their growth potential will be limited. The development of robust and reliable electric vehicle charging infrastructure is essential for EVs to reach their full potential. This article will explore various aspects of electric vehicle charging infrastructure, including companies, grants, deployment guidelines, assessments, and even ETFs.
Types of Electric Vehicle Charging
There are three main types of electric vehicle charging: Level 1, Level 2, and Level 3 (also known as DC fast charging).
- Level 1 charging is the slowest method and uses a standard 120-volt household outlet. It typically provides around 4-5 miles of range per hour of charging, making it ideal for overnight charging at home.
- Level 2 charging is faster and requires a 240-volt outlet. It provides around 10-20 miles of range per hour of charging. Level 2 charging is suitable for home charging or public charging stations and is the most common type of charging available.
- Level 3 charging is the fastest and uses direct current (DC) to rapidly charge the battery. It can provide up to 80% of the battery's charge in as little as 30 minutes, but it requires specialized equipment and is usually found at public charging stations or along highways for long-distance travel.
EV Charging Network Providers
There are several EV charging network providers in the market, such as ChargePoint, Electrify America, EVgo, and Tesla Supercharger. These networks offer public charging stations, and some of them have mobile apps to locate charging stations, make payments, and monitor charging progress.
Charging at Home
Home charging is the most convenient and cost-effective way to charge an electric vehicle. For Level 1 charging, all you need is a standard 120-volt outlet. However, for Level 2 charging, you'll need a 240-volt outlet, which will require a professional installation. It's essential to hire a qualified electrician to install the outlet, as improper installation can be dangerous.
Most EVs come with a portable Level 1 charger, but for Level 2 charging, you'll need to purchase a charging station. Charging stations vary in price and features, but most cost between $500 and $1,500, and some can be eligible for tax credits.
Public Charging Stations
Public charging stations are available at various locations such as shopping centers, parking lots, and highways. Charging fees vary depending on the provider and location, but some stations offer free charging. The cost of charging is usually based on the amount of electricity used or the time spent charging.
It's essential to have the appropriate charging adapter for your vehicle when using a public charging station. Most charging stations will provide standard Level 2 charging, but some may also offer Level 3 DC fast charging. Make sure to check the station's compatibility before plugging in your EV.
Charging Time and Range
Charging time and range vary depending on the type of charging and the EV model. As mentioned earlier, Level 1 charging provides around 4-5 miles of range per hour of charging, while Level 2 charging provides around 10-20 miles of range per hour of charging. Level 3 DC fast charging can provide up to 80% of the battery's charge in as little as 30 minutes.
The range of an EV also depends on various factors such as battery size, driving habits, and weather conditions. EVs with larger batteries usually have a longer range, while driving at high speeds and using air conditioning or heating can decrease the range.
Conclusion
In conclusion, electric vehicle charging is a rapidly evolving technology that has significant implications for our environment, economy, and way of life. As more and more people adopt electric vehicles, the demand for convenient, reliable, and efficient charging infrastructure will only continue to grow. By understanding the different types of EV charging, their benefits, and their limitations, we can make informed decisions about which solutions best fit our needs and priorities.
Moreover, businesses that invest in EV charging infrastructure can benefit from increased foot traffic, customer loyalty, and brand recognition, while helping to create a more sustainable future. We hope this article has provided you with a useful overview of the electric vehicle charging landscape and inspired you to explore this exciting and rapidly expanding field.