Electric Cars as a Future Energy Accumulation System

Introduction
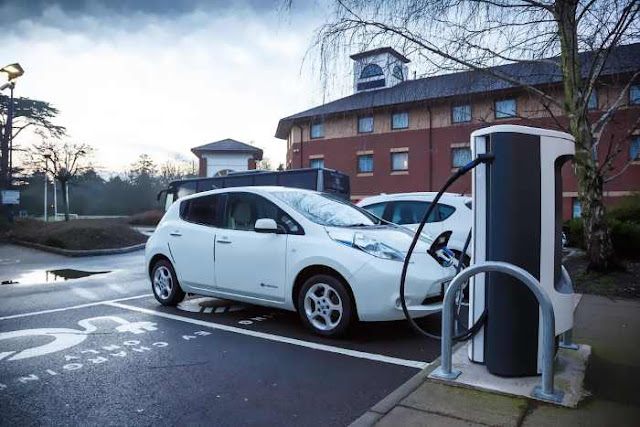
Use of electric cars in the system of electrical energy accumulation and power deficit tackling is a new issue consistent with the strategy of the EU intelligent development. The satisfactory level of electrical energy consumption/generation in Poland is estimated to be app. 150 TWh, as for technical conditions, the number of cars in Poland is defined to be more than 20 mln cars with the average power of 50 kW. The total power installed in automobiles (above 1000 Wh) is twenty five times higher than the power stored in the national power system (NPS *40 Wh), whereas, currently used cars with combustion engines and hybrid drives are absolutely not adjusted to perform prosumer tasks. Prime minister of the Republic of Poland, M. Morawiecki, thinks it is necessary to find a new, innovative solution to this problem, in Poland.
According to Mr Morawiecki’s plan, the government of Poland intends to encourage development of such a system. One of actions to be taken is creation of a market for electric cars. The Ministry of Energy predicts that in 2025 (in 8 years), in Poland, there can be million, and ultimately, with progressive implementation of innovation, even 20 mln such vehicles. It is said that the total demand for energy of 1 mln cars is app. 4 TWh yearly, and potentially, in case of power deficit the electric power grid can be provided with the same amount of energy. Energy is also accumulated in parts of cars and can be recovered. The strength and energy tests methodology of the car elements were described below. In Poland, electric cars, as prosumer tools, can in the future become an interesting source of electric power supply for the National Power System, at least 80 TWh yearly (4 TWhx20 mln automobiles).
Is this the right strategy?
The goal of this study is to indicate a possibility of providing Poland with power supply safety and efficiency with the use of electric cars (EC). It is assumed that, by connecting them to local power supply systems, occurrence of electrical power deficits can be prevented more effectively. Thus, electrical cars can improve the availability of power in the local power grids of the National Power System.
The System Elements and Relations
The concept of development, referred to as Morawiecki’s Plan, is fully consistent with the European policy which aims at supporting innovative solutions in economy. The priority of the government is to provide new industries with support by using results of research conducted in Polish research and development institutes.
The Polish Plan is based on three pillars. Flexibility and innovativeness of economy that are supposed to free the Polish economy from the constraint of medium profit and medium quality product. Industrialization 4G (fourth generation) is supposed to take into consideration all the elements of digital economy, and expansion and export are supposed to be a common goal of all the Middle and Eastern European countries which are too small to build their own economic growth on the basis of their domestic markets [6]. New possibilities that are provided by progress in motorization can connected with clean (mainly electrical) drives can be a real breakthrough. This, however, involves creating a new dedicated infrastructure prepared for cooperation with the local electric power grid.
Innovative sectors of economy, include: automotive industry: renewable energy sources, nanotechnologies, biotechnologies, information technologies power engineering technologies, quant engineering, spintronics, (mesoscopic electronics) and other high technology industries. One of the most attractive aspects of the contemporary innovation is a big variety of methods for perception, design, operation and use of standard transportation devices and energy machinery.
According to literature, in 2025, in Poland, the demand for heat and cold is estimated to be 240 TWh, the demand for fuel to be used by transportation— 210 TWh, for electrical energy—190 TWh. This data shows that gross demand for electrical energy in 2030 will increase by app. 54.2%, from the current level of 161 TWh up to 217.4 TWh. The highest increase is predicted in services (75%), in transportation (62%) and in households (34%). In industry the demand for electrical energy is predicted to be app. 28%, and in agriculture it will basically remain at the same level.
The most interesting solutions concerning polymodality (multi functionality) of car operation involves providing a vehicle, and especially its drive, with a new role and a new function to be performed in different energy technologies, that is, micro combined heat and power systems (mCHP), stations for battery charging and generation of energy from batteries, conversion of solar energy into electrical or heat energy, etc.
Information Source:
Haussmann, Peter, and Joachim Melbert. Sensorless Individual Cell Temperature Measurement by Means of Impedance Spectroscopy using Standard Battery Management Systems of Electric Vehicles. No. 2020-01-0863. SAE Technical Paper, 2020.